Melasma is a common skin condition that affects many individuals, particularly women. In this article, we will explore what melasma is, its causes, and effective treatment options to help you manage this condition.
What is Melasma?
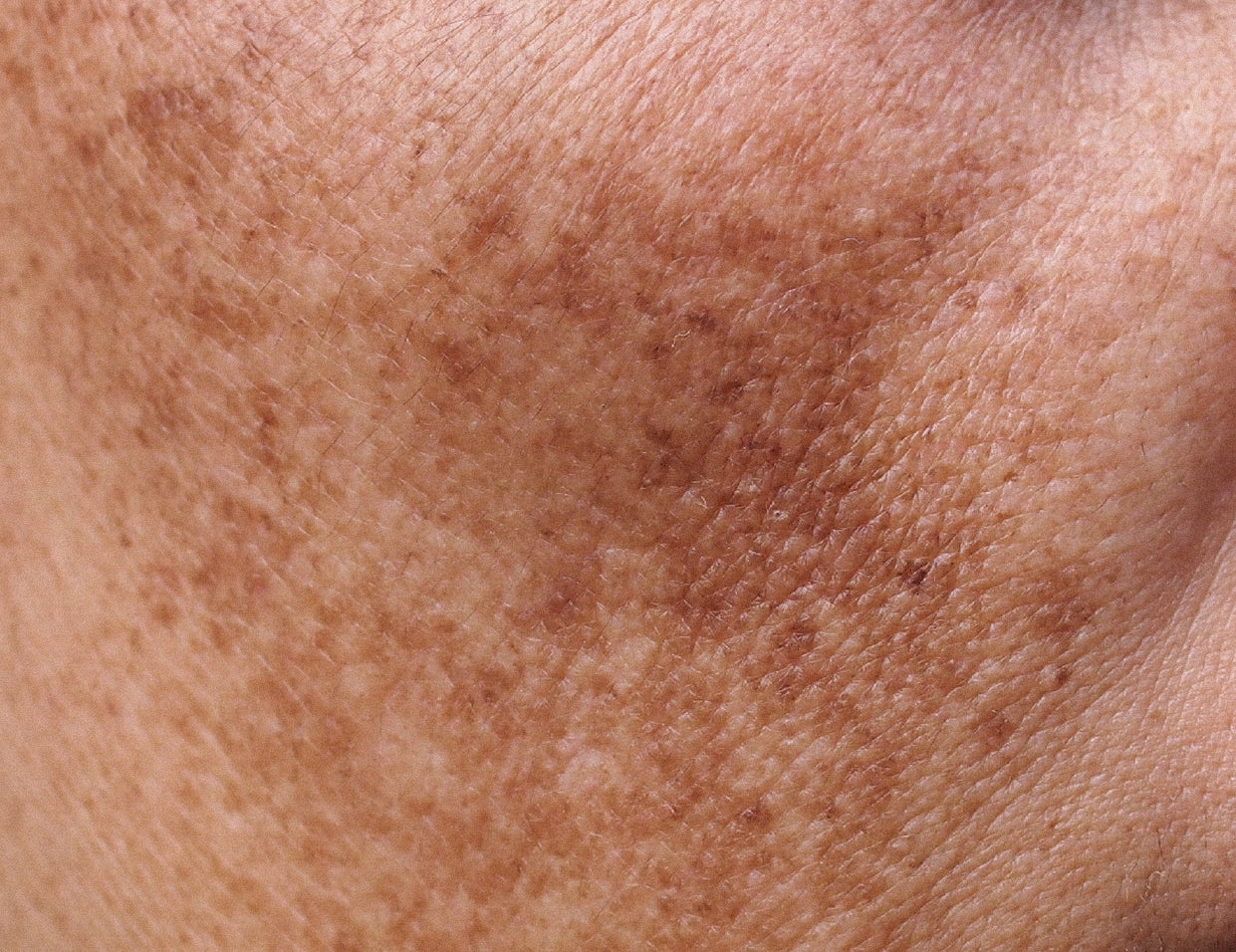
Melasma is characterized by the development of symmetrical, hyperpigmented patches on the skin, typically appearing on the face. However, it can also occur in other areas such as the neck, chest, and arms. Hyperpigmentation refers to darkened patches of skin that are darker than your natural skin tone. Melasma can appear brown, gray, or even bluish in color. Importantly, melasma is asymptomatic, meaning it does not cause itching or pain.
Causes of Melasma
Most individuals who develop melasma have a genetic predisposition to the condition. This means that there is something in their DNA that makes them susceptible to melasma triggers. One of the primary triggers is exposure to UV light or radiation. However, not everyone exposed to sunlight develops melasma, suggesting a genetic component.
In addition to UV light, certain populations may experience melasma triggered by blue light, which falls within the visible light spectrum. Hormonal shifts, specifically increased levels of estrogen and progesterone, also contribute to the development of melasma. Women often report their first melasma flare-ups after starting oral contraceptive pills or during pregnancy. Melasma is sometimes referred to as the "mask of pregnancy" due to its association with hormonal changes. It's important to note that progesterone therapy, including the use of the mini pill or hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs) like Skyla or Mirena, can also cause melasma. Recently, an increasing number of women in their 50s and 60s have been seeking treatment for melasma.
Treating Melasma
While melasma can be challenging to treat, there are various options available to help manage and reduce its appearance. Here are a few treatment approaches commonly used:
Sun Protection: Protecting your skin from UV exposure is crucial in managing melasma. Wear broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF daily, even on cloudy days, and reapply it every two hours. Additionally, use wide-brimmed hats and seek shade during peak sun hours.
Topical Agents: Dermatologists often recommend topical creams containing ingredients such as hydroquinone, retinoids, corticosteroids, or azelaic acid. These agents help lighten the dark patches and even out skin tone.
Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the top layers, revealing fresher, less pigmented skin. Medium to deep peels may be recommended for melasma treatment.
Laser Therapy: Certain laser treatments, such as fractional lasers can target and reduce melasma pigmentation. These procedures work by breaking down the excess melanin responsible for the dark patches.
Combination Therapy: In some cases, a combination of treatments may be recommended to achieve optimal results. Your dermatologist can create a personalized treatment plan based on your specific needs.
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by symmetrical hyperpigmented patches, predominantly seen in women. Although its exact causes are not fully understood, genetic predisposition, UV and blue light exposure, and hormonal shifts play significant roles. While melasma can be frustrating, various treatment options are available to help manage and improve its appearance. Consult with a dermatologist to determine the most suitable treatment approach for your melasma.
Remember, consistency and patience are key when treating melasma. With proper care, you can effectively reduce the visibility of melasma and achieve a more even complexion.